Slash Commands
Slash commands are used to quickly add components to the content.
When starting a new line in Dhub editor you should see a suggestion like this:

After typing a single / (forward slash) a menu will pop-up with all the available commands:
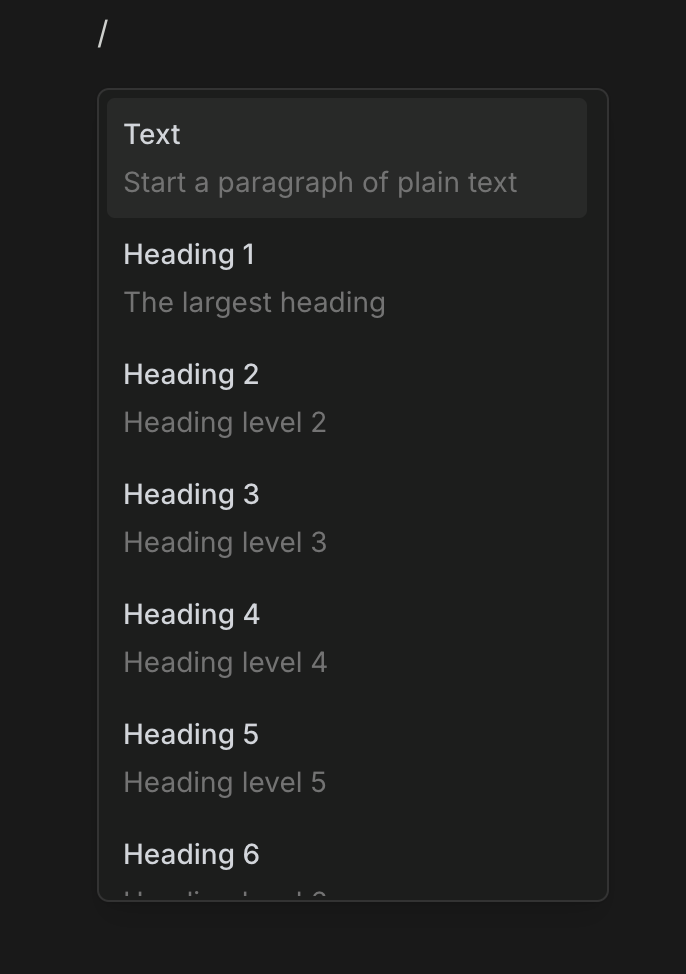
Picking a slash command
After typing /, click on any option in the menu and editor will add that component.
For instance, after clicking on Heading 2, the current line will be a heading with larger font than body text.
Headings are not to be overlooked - they're used to divide content into semantic sections and play a huge role for SEO.
For example, there should be only one Heading 1 per page.
Using quick search
A very quick way to add components is to continue typing after the / and search for a command. Then hit Enter and voilà, the component is added to the editor!
For example:
-
typing
/imgwill show Image and Inline Image components. -
/h2will show Heading 2 -
/tablewill show Table component -
/calloutwill allow to add a Callout component
There's no need type the full command name. To write content fast use short versions, like /tbl to find Table or /quo for a Quote.
No need to memorize these, the search is fuzzy. Both /h2 or /hd2 would work.
You can use up and down arrow keys to select a command in the list. Once selected, press Enter to add it to the content.
Changing current component
Let's say we wrote /callout and added it to the document. But then changed our minds and decided that a regular text is fine
To change the Callout back to regular text, go to the start of the line and type /text :
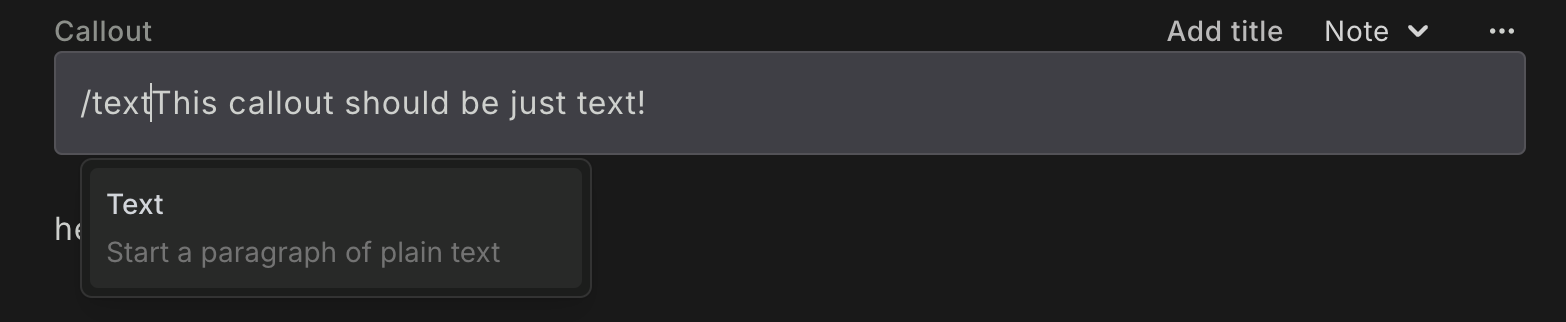
After pressing Enter or clicking the Text option in the slash command menu, the callout will be changed to regular text.
This works with other components too. This allows to quickly switch simple text to Callout or Quote, or Heading and etc.
List of all commands
Below is a list of all available slash commands in Dhub editor. This list is always growing so be sure to check back later for new stuff!
/text
| Component | Slash command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Text | /text | Start a paragraph of plain text |
| Divider | /divider | Visually divide your content |
| Heading 1 | /heading 1 or /h1 | The largest heading |
| Heading 2 | /heading 2 or /h2 | Heading level 2 |
| Heading 3 | /heading 3 or /h3 | Heading level 3 |
| Heading 4 | /heading 4 or /h4 | Heading level 4 |
| Heading 5 | /heading 5 or /h5 | Heading level 5 |
| Heading 6 | /heading 6 or /h6 | Heading level 6 |
| Bulleted list | /bullet or /blt or /list | Create a bulleted list for unordered items |
Numbered list | /number or /nmb | Create a numbered list for ordered items |
| Quote | /quote or /qt | Add a quotation |
| Code block | /code or /cd | Create a code snippet |
| Image | /image or /img | Add standalone image which can take full width of the content. |
| Inline image | /inline or /iimg | Add image which flows along with the text. Useful for smaller images like icons. |
| Callout | /callout or /call | Add a more prominent block of text. |
| Table | /table or /tbl | Structure your data into a table |
| Embedded MDX | /embed or /mdx | Embed code directly into Markdown. Useful for adding custom code like |
| Frontmatter variables | /front or /vars | Insert frontmatter variables at the top of the document. This is sometimes used to set the document title, author, date of publishing and other fields. |